Clasificación
Los dicloroacetatos son sales de ácido dicloroacético. Ambas, sales y ácidos son químicos producidos por el hombre. El DCA es un producto de la desinfección clorina del agua.1, 2 El DCA es un polvo que puede ser almacenado en forma de píldora.
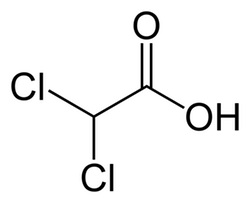
El ácido dicloroacético es típicamente fabricado para propósitos industriales. Debido a que la forma ácida (mostrada en la parte superior) causa quemaduras severas, el dicloroacetato de sodio (DCA), está siendo estudiado como un posible fármaco.3 A finales del siglo 20th, se encontró que el DCA reducía los niveles elevados de azúcar en la sangre en diabéticos. 4 El DCA bloquea una enzima clave (quinasa piruvato deshidrogenasa) en la vía metabólica que produce energía utilizable a partir del azúcar.5
Investigación Científica
DCA y desórdenes metabólicos
DCA y tratamiento contra el cáncer
DCA como un potencial agente causante de cáncer (carcinógeno)
De acuerdo a la Agencia de Protección Ambiental de los E.E.U.U. (EPA), el DCA es carcinógeno en ratones y ratas de laboratorio. Varios estudios han mostrado que el DCA causa cáncer en animales de laboratorio.24, 25, 26 Aún no han habido suficientes estudios para determinar si el DCA causa cácer en humanos, pero basándose en los resultados en animales, la EPA considera que es 'probable' que el DCA cause cáncer en humanos.27
Aprobación de la Administración de Alimentos y Fármacos de los E.E.U.U.
No existe evidencia suficiente que apoye que el dicloroacetato sea efectivo en la lucha contra el cáncer y aún no ha sido aprobado por la FDA como tratamiento contra el cáncer.
- 1 Miller JW, Uden PC. Characterization of nonvolatile aqueous chlorination products of humic substances. Environ Sci Technol. 1983 Mar 1;17(3):150-7 [PUBMED]
- 2 Uden, Peter C., Miller, Joel W. Clorinated acids and chloral in drinking water. (1983) Journal / American Water Works Association, 75 (10), pp. 524-527.
- 3 Material Safety Data Sheet on DCA (Glen Research). 3/24/2009 [http://www.glenresearch.com/MSDS/reagents/m40-4044-XX.pdf]
- 4 Stacpoole PW, Greene YJ. Dichloroacetate. Diabetes Care. 1992 Jun;15(6):785-91. [PUBMED]
- 5ab Stacpoole PW. The pharmacology of dichloroacetate. Metabolism. 1989 Nov;38(11):1124-44. [PUBMED]
- 6 Abdelmalak M, Lew A, Ramezani R, Shroads AL, Coats BS, Langaee T, Shankar MN, Neiberger RE, Subramony SH, Stacpoole PW. Long-term safety of dichloroacetate in congenital lactic acidosis. Mol Genet Metab. 2013 Apr 6. pii: S1096-7192(13)00108-X. [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 7 Kerr DS. Review of clinical trials for mitochondrial disorders: 1997-2012. Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Apr;10(2):307-19. [PUBMED]
- 8ab Sutendra G, Michelakis ED. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase as a novel therapeutic target in oncology. Front Oncol. 2013;3:38 Epub 2013 Mar 7. [PUBMED]
- 9 Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y, Carew JS, Feng L, Bhalla KN, Keating MJ, Huang P. Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia. Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 15;65(2):613-21. [PUBMED]
- 10ab Fujiwara S, Kawano Y, Yuki H, Okuno Y, Nosaka K, Mitsuya H, Hata H. PDK1 inhibition is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 2013 Jan 15;108(1):170-8. Epub 2012 Nov 29. [PUBMED]
- 11 Shen YC, Ou DL, Hsu C, Lin KL, Chang CY, Lin CY, Liu SH, Cheng AL. Activating oxidative phosphorylation by a pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor overcomes sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013 Jan 15;108(1):72-81. Epub 2012 Dec 20. [PUBMED]
- 12 Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Kinnaird A, Stenson TH, Haromy A, Parker JM, McMurtry MS, Michelakis ED. Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1a signaling and angiogenesis in cancer. Oncogene. 2013 Mar 28;32(13):1638-50. Epub 2012 May 21. [PUBMED]
- 13 Fiebiger W, Olszewski U, Ulsperger E, Geissler K, Hamilton G. In vitro cytotoxicity of novel platinum-based drugs and dichloroacetate against lung carcinoid cell lines. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011 Jan;13(1):43-9. [PUBMED]
- 14 Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR, Board PG, Blackburn AC. Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Feb;120(1):253-60. Epub 2009 Jun 19. [PUBMED]
- 15ab Vella S, Conti M, Tasso R, Cancedda R, Pagano A. Dichloroacetate inhibits neuroblastoma growth by specifically acting against malignant undifferentiated cells. Int J Cancer. 2012 Apr 1;130(7):1484-93. Epub 2011 Aug 27 [PUBMED]
- 16 Cao W, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, Namiki K, Sakai Y, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C, Rosser CJ. Dichloroacetate (DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate. 2008 Aug 1;68(11):1223-31. [PUBMED]
- 17 Wong JY, Huggins GS, Debidda M, Munshi NC, De Vivo I. Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2008 Jun;109(3):394-402. Epub 2008 Apr 18. [PUBMED]
- 18 Shahrzad S, Lacombe K, Adamcic U, Minhas K, Coomber BL. Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) reduces apoptosis in colorectal tumor hypoxia. Cancer Lett. 2010 Nov 1;297(1):75-83. Epub 2010 May 26. [PUBMED]
- 19 Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Karioti A, Antoniadi G, Antoniadis N, Liakopoulos V, Stefanidis I. Dichloroacetate at therapeutic concentration alters glucose metabolism and induces regulatory T-cell differentiation in alloreactive human lymphocytes. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Apr 13:1-6. [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 20 Ohashi T, Akazawa T, Aoki M, Kuze B, Mizuta K, Ito Y, Inoue N. Dichloroacetate improves immune dysfunction caused by tumor-secreted lactic acid and increases antitumor immunoreactivity. Int J Cancer. 2013 Feb 19 [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 21ab Michelakis ED, Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Webster L, Haromy A, Niven E, Maguire C, Gammer TL, Mackey JR, Fulton D, Abdulkarim B, McMurtry MS, Petruk KC. Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med. 2010 May 12;2(31):31ra34 [PUBMED]
- 22 Flavin DF. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Reversal with Dichloroacetate. J Oncol. 2010;2010. pii: 414726. Epub 2010 Sep 16. [PUBMED]
- 23 Calcutt NA, Lopez VL, Bautista AD, Mizisin LM, Torres BR, Shroads AL, Mizisin AP, Stacpoole PW. Peripheral neuropathy in rats exposed to dichloroacetate. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 Sep;68(9):985-93. [PUBMED]
- 24 DeAngelo AB, Daniel FB, Stober JA, Olson GR. The carcinogenicity of dichloroacetic acid in the male B6C3F1 mouse. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1991 Feb;16(2):337-47. [PUBMED]
- 25 DeAngelo AB, Daniel FB, Most BM, Olson GR. The carcinogenicity of dichloroacetic acid in the male Fischer 344 rat. Toxicology. 1996 Dec 18;114(3):207-21. [PUBMED]
- 26 International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization. IARC mongraphs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Volume 84 (2004) [http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol84/mono84-10.pdf]
- 27 EPA Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) sheet on Dichloroacetic acid (CASRN 79-43-6) [http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0654.htm]