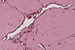
Tumors need blood in order to survive; blood provides nutrients critical for growth and proliferation. For this reason many cancer treatments have been developed to target blood vessel growth (angiogenesis). Unfortunately, the available drugs are only partially effective.
Researchers from Switzerland and the UK have developed a new way of attacking tumor blood vessels that seems to be more effective than existing therapies. The researchers used an antibody targeted against a protein in the tumor vessels. They modified the antibody by attaching a chemical that can kill cancer cells when it is exposed to light of a specific type. The treatment was very effective in mouse models and should be particularly useful for cancers of the skin, that allow for exposure to the required light.
