Brigatinib
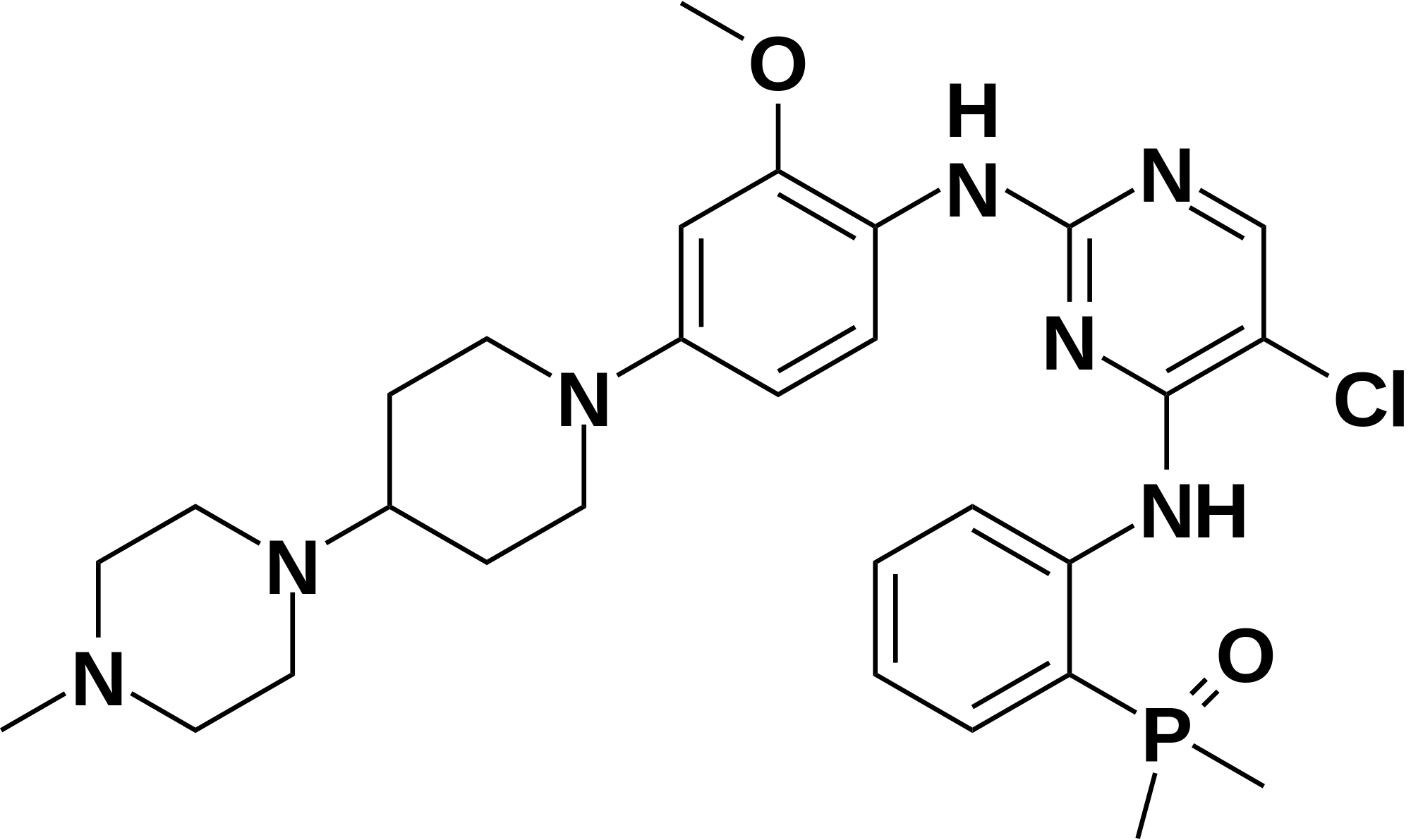
Brigatinib is a small molecule targeted cancer therapy used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Brigatinib has exhibited activity as a strong inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) (cancerous cell proteins) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which in turn leads to decrease in cancerous cells and overall apoptosis.1
- 1 Health Care Professionals Information. (n.d.). Retrieved July 19, 2017, from https://www.alunbrig.com/hcp?utm_source=google&utm_medium=cpc&utm_term=brigatinib%2Bmechanism%2Bof%2Baction&utm_campaign=GS%2B-%2BNA%2B-%2BBR%2B-%2BGeneric%2B-%2BHCP_GS%2B-%2BInformation_EX
The most serious side effects of brigatinib include: swelling of the lungs (if extremely severe seek medical attention), high blood pressure, slow heart rate, vision problems and tenderness/weakness. However, the most common side effects include: nausea, diarrhea, stomach problems and headache.1
- 1 Patient Information. (n.d.). Retrieved July 19, 2017, from https://www.alunbrig.com/
Patients with prior lung or breathing problems should alert their physician before starting a Brigatinib prescription. Women who are pregnant or are looking to become pregnant should be especially careful in taking Brigatinib.1
- 1 Patient Information. (n.d.). Retrieved July 19, 2017, from https://www.alunbrig.com/
