Meperidine
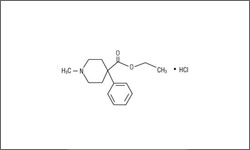
Meperidine is a narcotic analgesic with actions similar to morphine. It binds primarily to the mu opioid receptor to relieve pain, which changes the way the body senses pain.1
The molecular structure below shows the 3D conformer Meperidine.
- 1 Meperidine. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682117.html
The most common side effects include light-headedness and dizziness, sedation or drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, sweating. Meperidine can be habit-forming. Psychological and physiological withdrawal symptoms can occur if the patient becomes drug dependent. With prolonged use, tolerance may also become a problem, requiring higher dosages to achieve pain relief. Alcohol can intensify some of the mental and emotional side effects of meperidine, such as drowsiness and changes in mood. Patients should avoid alcohol consumption while taking meperidine. It can aslo cause respiratory depression. This may result in a potentially dangerous slowing of a patient's breathing rate.1
- 1 Meperidine. MedlinePlus. 2016. https://medlineplus.gov/druginfo/meds/a682117.html
