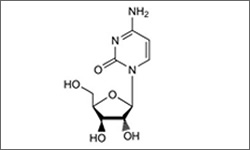
Arabinosylcytosine, Cytarabine
Malignancies for which cytarabine is used include: Acute non-lymphocytic leukemia, Acute lymphocytic leukemia and Chronic myelocytic leukemia. Cytarabine (Cytosar®, ara-C) is administered as an infusion or as in injection under the skin.
Cytarabine (Cytosar®, ara-C) is an antimetabolite that acts as a pyrimidine antagonist. It is thought that its primary activity is interrupting DNA synthesis.
The molecular structure above shows Arabinosylcytosine, Cytarabine.
Common side effects include: bone marrow suppression, anorexia, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, oral/anal inflammation or ulceration, rash, fever. Cytarabine (Cytosar®, ara-C) is a suppressor of bone marrow activity. It is important to monitor blood cell and platelet counts throughout the duration of treatment with blood tests done often. 1
- 1 Cytosar. Product Monograph. Pfizer. September, 2014. [http://www.pfizer.ca/sites/g/files/g10017036/f/201410/cytosar-non-annotated-pm-175940-E.pdf]
Cytarabine should not be taken by women who are pregnant and patients should not become pregnant while using this drug, as it may have harmful affects on the developing fetus. 1
- 1 Cytosar. Product Monograph. Pfizer. September, 2014. [http://www.pfizer.ca/sites/g/files/g10017036/f/201410/cytosar-non-annotated-pm-175940-E.pdf]
