Ifosfamide
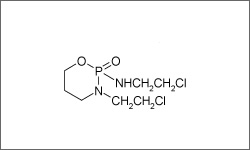
Ifosfamide (Ifex®) is an alkylating agent used mainly to treat germ cell testicular cancer. Other malignancies for which ifosfamide is used include: soft tissue sarcoma, acute lymphocytic leukemia, bladder cancer, bone cancer, pancreatic cancer, stomach cancer, breast cancer, cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, lung cancer, ovarian cancer, neuroblastoma, lymphoma, Wilms' tumor. Ifosfamide is usually administered in injection form.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Ifosfamide is activated by the liver cytochrome P450 microsomal system, which binds with nucleic acids by cross-linking of DNA and RNA and leads to inhibition of protein synthesis.1
The diagram above shows the 3D molecular structure of Ifosfamide.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include alopecia (hair loss), temporary ridging of the nails, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, depression of blood cell counts. Less common side effects include: temporary toxicities, changes in liver function, skin rashes or darkening, confusion, lethargy, sleepiness, and loss of balance.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
A very serious problem that may result with treatment is hemorrhagic cystitis, which is prevented by administering ifosfamide in combination with a compound called Mesna (Uromitexan, Mesnex), which inactivates the toxic compounds, minimizing the problem. Patients considering ifosfamide as cancer therapy should talk to their doctor about the drug's effects on fertility, potential or current pregnancy, breast-feeding, chickenpox status, shingles status, kidney disease, liver disease, and all other medications currently taken.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
