Rituximab
In 1997, rituximab became the first antibody approved for the treatment of cancer in the United States. Rituximab is used in the treatment of low-grade relapsed or refractory (treatment resistant) Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, as well as CLL. Rituximab is administered as an IV infusion once a week usually for 4 to 8 doses.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
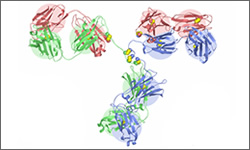
Rituximab is a genetically engineered monoclonal antibody containing both human and mouse components. It is directed against the CD20 antigen. The CD20 protein is present on the majority of mature B-cells but not on B-cells in the bone marrow. The drug allows the repopulation of the blood with B-cells after treatment ends. Binding of the antibody stimulates the destruction of the tagged cells. Evidence also suggests that rituximab may induce apoptosis in cells. Note that the image shown is a general structure of an antibody. There are four proteins bound together in a 'Y' shape. The two top tips of the Y are where the antibody binds with its target. This means that each antibody molecule can bind to two identical target regions.1
The diagram above shows the 3D molecular structure of Rituximab.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
The most common side effects include fever, chills, infection, lowered lymphocyte count. Infusion reactions may also occur. During the first infusion many patients experience such a reaction with fever and chills. These symptoms can be treated with other medications or by slowing or stopping the infusion. Other, more severe reactions may also occur. Some patients may also experience pulmonary side effects that include cough and rhinitis. Other patients may experience more severe side effects. 1
- 1 Rituxan.. Prescribing Information. IDEC Pharmaceuticals Corporation. 2016. [http://www.rituxan.com]
