Carboplatin
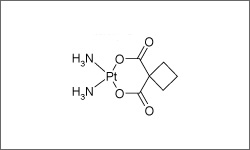
Carboplatin (Paraplatin®) is an alkylating agent used to treat a variety of cancers. Malignancies for which carboplatin is used include: Ovarian cancer, Germ cell tumors, Head and neck cancer, Small cell and non-small cell lung cancer, Bladder cancer, Relapsed and refractory (resistant to ordinary treatment) acute leukemia, endometrial cancer. Carboplatin is usually administered intravenously.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Carboplatin bind covalently to DNA and reacts with intrastrand and interstrand DNA sites to inhibit production of proteins, while also inhibiting transcription.1
The diagram above shows the 3D molecular structure of Carboplatin.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include decreased white blood cell count with increased risk of infection, decreased platelet count with increased risk of bleeding, brittle hair, altered kidney function (at high doses), fetal abnormalities may occur if the patient is pregnant or becomes pregnant during treatment. Frequent side effects also include: nausea, vomiting and possible allergic reaction.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
