Chlorambucil
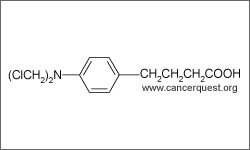
Chlorambucil is an alkylating agent that is used to treat a variety of cancer types. Malignancies for which chlorambucil is use include chronic lymphocytic leukemia, lymphomas, Hodgkin's disease. Chlorambucil is usually administered as an intravenous infusion or in tablet form.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Aromatic analog of nitrogen mustard functions as a alkylating agent, which forms cross-links with DNA. This leads to inhibition of DNA synthesis and activity on all phases of the cancer cell cycle.1
The diagram above shows the 3D molecular structure of Chlorambucil.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, oral ulcers. Less common side effects include tremors, twitching, seizures, other abnormal activity of the nervous system, and also changes in and allergic reactions of the skin. Chlorambucil should not be taken by women who are pregnant and patients should not become pregnant while using this drug, as it may have harmful affects on the developing fetus. This drug may also have negative effects on fertility in the years following treatment. Bone marrow depression is the most common toxicity associated with chlorambucil's usage. It is important to monitor the levels of white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin. 1
- 1 Leukeran.. Prescribing Information. GlaxoSmithKline. 2016. [http://www.gsk.com]
