Cisplatin
Cisplatin (Platinol®) is an alkylating agent used to treat a variety of cancers. Malignancies for which cisplatin is used include: Testicular cancer, Ovarian cancer, Bladder cancer, Head and neck cancer, Esophagus cancer, Small cell and non-small cell lung cancer, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Trophoblastic neoplasms. Cisplatin is typically administered intravenously over 1 or more hours.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Cisplatin is an alkylating agent that creates fragmented DNA, prevents DNA synthesis via cross-linking of DNA, and creates mutations in nucleotides.1
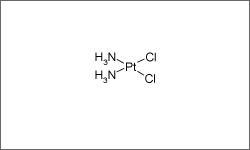
The diagram below shows the 3D molecular structure of Cisplatin.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include: kidney damage, decreased blood levels of magnesium, potassium, and calcium, nausea and vomiting, taste changes, including metallic taste to foods, sensation of 'pins and needles' in hands and/or feet, decreased red blood cell counts. Birth defects could occur if patient is pregnant while on treatment. The patient should have no immunizations (vaccinations) during and after treatment without prior discussion with the health care provider. Contact with people who have recently taken the oral polio vaccine should be avoided as directed by the health care provider. Kidney damage caused by cisplatin may be prevented by checking kidney function prior to administering the drug, giving extra intravenous fluids, and drinking extra fluids after the drug is given.1
- 1 Platinol.. Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. 2016. [http://packageinserts.bms.com/pi/pi_plavix.pdf]
