Dacarbazine
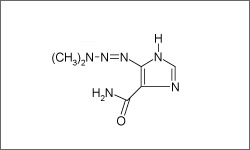
Dacarbazine (DTIC-Dome®) has anti tumor properties, which are metabolically activated. Decarbazine also methylates nucleic acids, while inhibiting DNA and protein synthesis.1
The molecular structure below shows the 3D conformer Dacarbazine.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include: extreme nausea and vomiting, anorexia, hair loss, and facial flushing. Dacarbazine should not be taken by women who are pregnant and patients should not become pregnant while using this drug, as it may have harmful effects on the developing fetus. Bone marrow depression is the most common toxicity associated with dacarbazine usage. It is important to monitor the levels of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. 1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
