Daunorubicin
Daunorubicin is used to treat acute nonlymphocytic leukemia in adults and acute lymphocytic leukemia in adults and children. It is administered in an intravenous infusion.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Daunorubicin (Cerubidine®) is an anti tumor antibiotic that exerts its effects on cancer cells primarily through two mechanisms. Intercalation occurs when the drug wedges between the bases of DNA. This blocks DNA from being copied (replication) or being used to make proteins. The drug also inhibits (reduce) the activity of an enzyme, topoisomerase type II. This leads to breaks in the genomic DNA.1
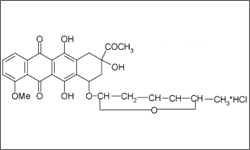
The structure below shows the molecular diagram of Daunorubicin.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include: bone marrow suppression, nausea and vomiting (near time of treatment), hair loss, infection due to bone marrow suppression, abdominal cramps and diarrhea.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Daunorubicin should not be taken by women who are pregnant and patients should not become pregnant while using this drug, as it may have harmful affects on the developing fetus. This drug may have effects on fertility after treatment has ended. Patients should note that after an infusion the urine may have a temporary red tinting. Daunorubicin is a strong suppressor of bone marrow activity. It is important to monitor blood cell and platelet counts throughout the duration of treatment. Daunorubicin may also have toxic effects on other systems, therefore, renal (kidney) function, and hepatic (liver) function tests should be performed routinely. Also, cardiac function must be monitored to avoid irreversible effects of toxicity. Evaluations of the function of these systems should be made before each infusion.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
