Exemestane
Exemestane (Aromasin®) is used in treatment of advanced breast cancer in postmenopausal women, only after their disease has progressed poorly following tamoxifen therapy. Exemestane is orally administered once daily after a meal.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Exemestane (Aromasin®) binds irreversibly (permanently) to the aromatase enzyme. This stops aromatase from making estrogen by stopping the conversion of adrenal androgens, which prevents the growth of estrogen dependent cancer.1
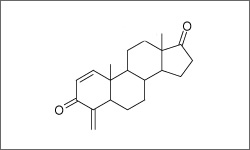
The structure below shows the breast cancer drug Aromasin, also known as Exemestane.
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Common side effects include: hot flashes, nausea, fatigue, eye disturbances, headaches dizziness, insomnia, depression, hypertension, joint pain, limb pains, back pains and osteoarthritis. There are no studies for aromasin in pregnant women yet. It is recommended only for postmenopausal women. If exposed to aromasin while pregnant, patients should contact a physician to assess the potential hazard to the fetus and possible risk of pregnancy loss.1
- 1 Chu, E., & DeVita, V. T. (2015). Physicians' cancer chemotherapy drug manual 2015. Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
