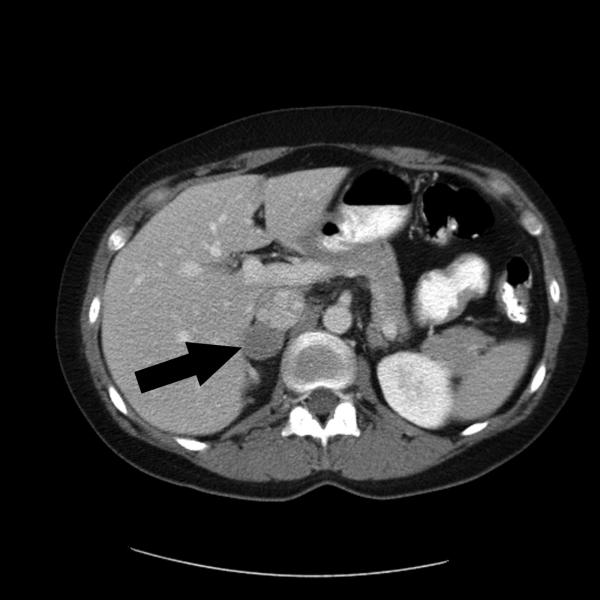
This image is a SPECT image that shows a rare adrenaline-producing tumor called adrenal pheochromocytoma.
SPECT/CT (SPECT=single photon emission computed tomography) imaging is used to measure some body functions and can be used to detect cancer. Patients are injected with a small amount of radioactive material and then have to lie in a machine that captures the gamma ray emissions from the material. The images that are created represent thin 'slices' through the body. Computer software is then used to combine the slices to make a virtual three dimensional model that can be viewed from any angle. SPECT can be used in combination with other imaging techniques (MRI, PET, etc.) to get additional details of the patient's status.1, 2
SPECT can be used to locate cancer, and monitor blood flow and brain activity.3, 4, 5 Research into the use of SPECT for different cancer types is ongoing. One possible benefit of SPECT is a higher sensitivity in the detection of cancer in specific cancer types and patient populations. For example, in one study, SPECT showed a better detection rate of sentinel nodes in breast cancer, specifically in obese patients.6
- 1 Spanoudaki VC, Ziegler SI. PET & SPECT instrumentation. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;(185 Pt 1):53-74. [PUBMED]
- 2 Delbeke D, Schöder H, Martin WH, Wahl RL. Hybrid imaging (SPECT/CT and PET/CT): improving therapeutic decisions. Semin Nucl Med. 2009 Sep;39(5):308-40. Review. [PUBMED]
- 3 Schillaci O. Single-photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography in lung cancer and malignant lymphoma. Semin Nucl Med. 2006 Oct;36(4):275-85. [PUBMED]
- 4 Dobrucki LW, Sinusas AJ. PET and SPECT in cardiovascular molecular imaging. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010 Jan;7(1):38-47. Epub 2009 Nov 24. [PUBMED]
- 5 Richardson M. Update on neuroimaging in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother. 2010 Jun;10(6):961-73. [PUBMED]
- 6 Hedva Lerman, Gennady Lievshitz1, Osnat Zak, Ur Metser1, Shlomo Schneebaum3, Einat Even-Sapir1. "Improved Sentinel Node Identification by SPECT/CT in Overweight Patients with Breast Cancer." Journal of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 48 No. 2 201-206. [PUBMED]
