Classification
Dicholoroacetates are salts of dichloroacetic acid. Both the salt and acid are man-made chemicals. DCA is a by-product of the chlorine disinfection of water.1, 2 DCA is a powder that can be made into pill form.
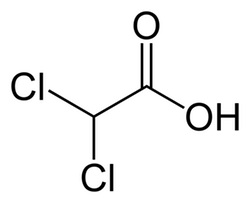
Dichloroacetic acid is typically manufactured for industrial purposes. Because the acid form (shown above) causes severe burns, only the salt, sodium dichloroacetate (DCA), is being studied as a possible drug.3 In the late 20th century, DCA was found to decrease high blood sugar levels in diabetics.4 DCA blocks a key enzyme (pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase) in the metabolic pathway that produces usable energy from sugar.5
Scientific Research
DCA and metabolic disorders
Because of its effects on how sugar is used by the body, DCA has been/is being studied as a possible treatment for some metabolic diseases, including lactic acidosis.5, 6, 7
DCA and cancer treatment
DCA's effects on energy production pathways led to studies examining the effects of DCA on cancer cells in animals and people (in vivo) and in the laboratory (in vitro). The work has focused on the chemical's ability to block an abnormal metabolic process that occurs in many cancer cells (called aerobic glycolysis or the "Warburg effect") and to "reactivate" nonfunctional mitochondria.8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Studies suggest that DCA-mediated changes lead to reduced blood vessel development (angiogenesis) in tumors.9, 13
DCA's anti-cancer activity has been studied with cells (and a few patients) from a number of cancer types, including lung carcinoid,14 breast cancer,15 neuroblastoma,16 prostate cancer,17 multiple myeloma,11 kidney cancer,18 and endometrial cancer.19 It seems to exert potent anti-cancer effects especially in conjunction with Metformin.20, 21
DCA may even be used in combination with standard treatments. Research suggests that it can increase the effectiveness of radiation on cancer cells,22 decrease the side effects associated with chemotherapy,23 and prevent cancer from recurring after surgery.24
Cancer cells from different types of cancer (i.e. breast vs lung vs liver) and even those from the same patient can be very different from each other. Research with neuroblastoma suggests that the differences seen between cancer cells can affect the effectiveness of DCA. As an example, the chemical has greater effects on undifferentiated, fully proliferating, more malignant neuroblastoma cancer cells than on differentiated and less malignant cells of the same type.16
However, in some systems DCA has been shown to PROTECT cancer cells from death. In research with colon cancer cells, DCA prevented the death of the cells in the laboratory and in animals.25 In mice with neuroblastoma, DCA enhanced the growth of tumor cells.26 Another study showed mixed results: DCA did not slow down tumor growth in mice, though it did make it harder for cancerous cells to spread (metastasize).27
DCA and the immune system
The effects of DCA on the immune system are being studied and are not yet clear. One study suggests that DCA may decrease the immune response against cancer by altering the activity of T lymphocytes, while other research has shown that DCA could increase immune function in tumors by reducing lactic acid levels in the tumor environment.28, 29
Clinical Trials
Despite the research done so far, relatively little is known about DCA as a cancer treatment in patients. A Canadian trial on 5 glioblastoma patients demonstrated some responses, but the information is difficult to interpret because the patients were also given other treatments and/or had failed previous treatments.30 There is a single report of a patient with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma who entered remission after treatment with DCA (after failing to respond to treatment with chemotherapy).31 Currently, there are several active clinical trials examining the effects of DCA on different cancer types. Some Phase I trials are complete, but study results have not been posted.32
View DCA clinical trials for cancer.
Side effects of DCA
A potentially dangerous side effect of DCA treatment is nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy). The mechanisms by which DCA induces peripheral neuropathy are not completely known, but DCA-induced neuropathy often limits the use of DCA in the treatment of patients.30, 33
DCA as a potential cancer causing agent (carcinogen)
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), DCA is carcinogenic in laboratory mice and rats. Several studies have shown that DCA causes cancer in lab animals.34, 35, 36 There have not been enough studies to determine whether DCA causes cancer in humans, but based on the results in animals, the EPA considers it ‘likely’ that DCA can cause cancer in humans.37
US Food and Drug Administration Approval
There is not enough evidence that dichloroacetate is effective in the fight against cancer, and it has not been approved by the FDA for cancer treatment.
Please be sure to see our notice on complementary therapies. To better understand and evaluate the research described above, read our Introduction to Scientific Research.
- 1 Miller JW, Uden PC. Characterization of nonvolatile aqueous chlorination products of humic substances. Environ Sci Technol. 1983 Mar 1;17(3):150-7 [PUBMED]
- 2 Uden, Peter C., Miller, Joel W. Clorinated acids and chloral in drinking water. (1983) Journal / American Water Works Association, 75 (10), pp. 524-527.
- 3 Material Safety Data Sheet on DCA (Glen Research). 3/24/2009 [http://www.glenresearch.com/MSDS/reagents/m40-4044-XX.pdf]
- 4 Stacpoole PW, Greene YJ. Dichloroacetate. Diabetes Care. 1992 Jun;15(6):785-91. [PUBMED]
- 5ab Stacpoole PW. The pharmacology of dichloroacetate. Metabolism. 1989 Nov;38(11):1124-44. [PUBMED]
- 6 Abdelmalak M, Lew A, Ramezani R, Shroads AL, Coats BS, Langaee T, Shankar MN, Neiberger RE, Subramony SH, Stacpoole PW. Long-term safety of dichloroacetate in congenital lactic acidosis. Mol Genet Metab. 2013 Apr 6. pii: S1096-7192(13)00108-X. [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 7 Kerr DS. Review of clinical trials for mitochondrial disorders: 1997-2012. Neurotherapeutics. 2013 Apr;10(2):307-19. [PUBMED]
- 8 De Preter G, Neveu MA, Danhier P, Brisson L, Payen VL, Porporato PE, Jordan BF1, Sonveaux P, Gallez B. Inhibition of the pentose phosphate pathway by dichloroacetate unravels a missing link between aerobic glycolysis and cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 19;7(3):2910-20. [PUBMED]
- 9ab Sutendra G, Michelakis ED. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase as a novel therapeutic target in oncology. Front Oncol. 2013;3:38 Epub 2013 Mar 7. [PUBMED]
- 10 Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y, Carew JS, Feng L, Bhalla KN, Keating MJ, Huang P. Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia. Cancer Res. 2005 Jan 15;65(2):613-21. [PUBMED]
- 11ab Fujiwara S, Kawano Y, Yuki H, Okuno Y, Nosaka K, Mitsuya H, Hata H. PDK1 inhibition is a novel therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Br J Cancer. 2013 Jan 15;108(1):170-8. Epub 2012 Nov 29. [PUBMED]
- 12 Shen YC, Ou DL, Hsu C, Lin KL, Chang CY, Lin CY, Liu SH, Cheng AL. Activating oxidative phosphorylation by a pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase inhibitor overcomes sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2013 Jan 15;108(1):72-81. Epub 2012 Dec 20. [PUBMED]
- 13 Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Kinnaird A, Stenson TH, Haromy A, Parker JM, McMurtry MS, Michelakis ED. Mitochondrial activation by inhibition of PDKII suppresses HIF1a signaling and angiogenesis in cancer. Oncogene. 2013 Mar 28;32(13):1638-50. Epub 2012 May 21. [PUBMED]
- 14 Fiebiger W, Olszewski U, Ulsperger E, Geissler K, Hamilton G. In vitro cytotoxicity of novel platinum-based drugs and dichloroacetate against lung carcinoid cell lines. Clin Transl Oncol. 2011 Jan;13(1):43-9. [PUBMED]
- 15 Sun RC, Fadia M, Dahlstrom JE, Parish CR, Board PG, Blackburn AC. Reversal of the glycolytic phenotype by dichloroacetate inhibits metastatic breast cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Feb;120(1):253-60. Epub 2009 Jun 19. [PUBMED]
- 16ab Vella S, Conti M, Tasso R, Cancedda R, Pagano A. Dichloroacetate inhibits neuroblastoma growth by specifically acting against malignant undifferentiated cells. Int J Cancer. 2012 Apr 1;130(7):1484-93. Epub 2011 Aug 27 [PUBMED]
- 17 Cao W, Yacoub S, Shiverick KT, Namiki K, Sakai Y, Porvasnik S, Urbanek C, Rosser CJ. Dichloroacetate (DCA) sensitizes both wild-type and over expressing Bcl-2 prostate cancer cells in vitro to radiation. Prostate. 2008 Aug 1;68(11):1223-31. [PUBMED]
- 18 Kinnaird A, Dromparis P, Saleme B, Gurtu V, Watson K, Paulin R, Zervopoulos S, Stenson T, Sutendra G, Pink DB, Carmine-Simmen K, Moore R, Lewis JD, Michelakis ED. Metabolic Modulation of Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma with Dichloroacetate, an Inhibitor of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase. Eur Urol. 2016 Apr;69(4):734-44. [PUBMED]
- 19 Wong JY, Huggins GS, Debidda M, Munshi NC, De Vivo I. Dichloroacetate induces apoptosis in endometrial cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 2008 Jun;109(3):394-402. Epub 2008 Apr 18. [PUBMED]
- 20 Voltan R, Rimondi E, Melloni E, Gilli P, Bertolasi V, Casciano F, Rigolin GM, Zauli G, Secchiero P. Metformin combined with sodium dichloroacetate promotes B leukemic cell death by suppressing anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1. Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 3. [PUBMED]
- 21 Hong SE, Jin HO, Kim HA, Seong MK, Kim EK, Ye SK, Choe TB, Lee JK, Kim JI, Park IC, Noh WC. Targeting HIF-1¿ is a prerequisite for cell sensitivity to dichloroacetate (DCA) and metformin.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Jan 8;469(2):164-70. [PUBMED]
- 22 Shen H, Hau E, Joshi S, Dilda PJ, McDonald KL. Sensitization of Glioblastoma Cells to Irradiation by Modulating the Glucose Metabolism. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Aug;14(8):1794-804. [PUBMED]
- 23 Galgamuwa R, Hardy K, Dahlstrom JE, Blackburn AC, Wium E, Rooke M, Cappello JY, Tummala P, Patel HR, Chuah A, Tian L, McMorrow L, Board PG, Theodoratos A. Dichloroacetate Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity without Compromising Cisplatin Anticancer Properties. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Mar 9. [PUBMED]
- 24 Zhang Z, Liu S, Qi Y, Zhou D, Xie Z, Jing X, Chen X, Huang Y. Time-programmed DCA and oxaliplatin release by multilayered nanofiber mats in prevention of local cancer recurrence following surgery. J Control Release. 2016 May 21;235:125-133. [PUBMED]
- 25 Shahrzad S, Lacombe K, Adamcic U, Minhas K, Coomber BL. Sodium dichloroacetate (DCA) reduces apoptosis in colorectal tumor hypoxia. Cancer Lett. 2010 Nov 1;297(1):75-83. Epub 2010 May 26. [PUBMED]
- 26 Feuerecker B, Seidl C, Pirsig S, Bruchelt G, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R. DCA promotes progression of neuroblastoma tumors in nude mice. Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 15;5(2):812-20. [PUBMED]
- 27 Kolesnik DL, Pyaskovskaya ON, Boychuk IV, Dasyukevich OI, Melnikov OR, Tarasov AS, Solyanik GI. Effect of dichloroacetate on Lewis lung carcinoma growth and metastasis. Exp Oncol. 2015 Jun;37(2):126-9. [PUBMED]
- 28 Eleftheriadis T, Pissas G, Karioti A, Antoniadi G, Antoniadis N, Liakopoulos V, Stefanidis I. Dichloroacetate at therapeutic concentration alters glucose metabolism and induces regulatory T-cell differentiation in alloreactive human lymphocytes. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013 Apr 13:1-6. [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 29 Ohashi T, Akazawa T, Aoki M, Kuze B, Mizuta K, Ito Y, Inoue N. Dichloroacetate improves immune dysfunction caused by tumor-secreted lactic acid and increases antitumor immunoreactivity. Int J Cancer. 2013 Feb 19 [Epub ahead of print] [PUBMED]
- 30ab Michelakis ED, Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Webster L, Haromy A, Niven E, Maguire C, Gammer TL, Mackey JR, Fulton D, Abdulkarim B, McMurtry MS, Petruk KC. Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med. 2010 May 12;2(31):31ra34 [PUBMED]
- 31 Flavin DF. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Reversal with Dichloroacetate. J Oncol. 2010;2010. pii: 414726. Epub 2010 Sep 16. [PUBMED]
- 32 National Library of Medicine. (2016). ClinicalTrials.gov Retrieved June 20, 2016. [https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=controlled+amino+acid+therapy&Search=Search]
- 33 Calcutt NA, Lopez VL, Bautista AD, Mizisin LM, Torres BR, Shroads AL, Mizisin AP, Stacpoole PW. Peripheral neuropathy in rats exposed to dichloroacetate. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 Sep;68(9):985-93. [PUBMED]
- 34 DeAngelo AB, Daniel FB, Stober JA, Olson GR. The carcinogenicity of dichloroacetic acid in the male B6C3F1 mouse. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1991 Feb;16(2):337-47. [PUBMED]
- 35 DeAngelo AB, Daniel FB, Most BM, Olson GR. The carcinogenicity of dichloroacetic acid in the male Fischer 344 rat. Toxicology. 1996 Dec 18;114(3):207-21. [PUBMED]
- 36 International Agency for Research on Cancer/World Health Organization. IARC mongraphs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Volume 84 (2004) [http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol84/mono84-10.pdf]
- 37 EPA Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) sheet on Dichloroacetic acid (CASRN 79-43-6) [http://www.epa.gov/iris/subst/0654.htm]